Artificial Sweeteners for People with Diabetes - Benefits and Complications.Artificial Sweeteners for People with Diabetes - Benefits and Complications.
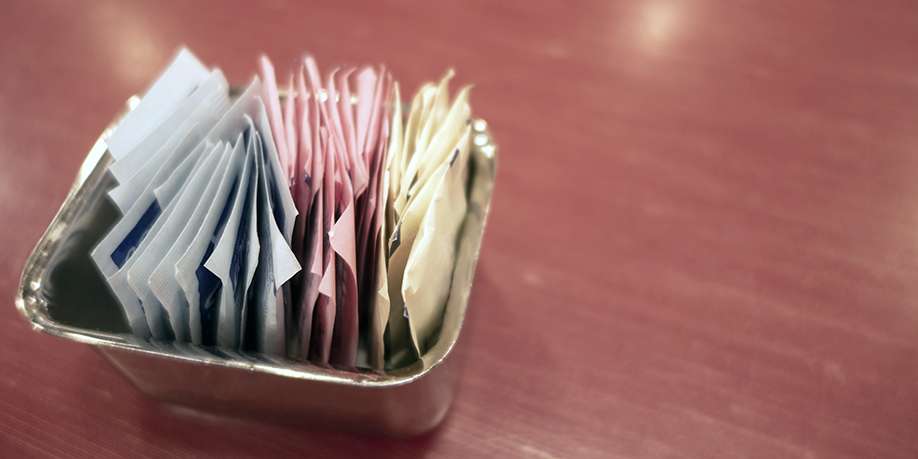  © Mirror Images | Dreamstime.com When the words “diabetes” and “table sugar” are used in the same sentence, the latter word is almost always used in a negative way. That is hardly surprising as the body of people with diabetes is unable to handle sugar that they consume normally, which means the body cannot convert sugar into energy the way it should. As a result, unprocessed sugar gets accumulated in the blood and causes a long list of health issues, some of which show themselves right away and some over time. To avoid or at least postpone the issues that diabetes can bring, you should take serious measures to control your sugar intake. This is not an easy mission as it involves exploring different treatment options that incorporate life habit changes and diet adjustments. In particular, one of the most important things is to curb your sweet tooth. That is easier said than done as people usually love sweets. This is where artificial sweeteners come into play. They don’t contain carbohydrates as regular sugar does, while most of them many times sweeter than sugar. Plus, they don’t have any calories too and there are quite a few of them available to choose from. Sounds exciting, isn’t it? Before drawing conclusions, let’s have a closer look at the subject of artificial sweeteners. Artificial sweeteners, or as they are also called, high-intensity sweeteners, offer the sweet taste of sugar, while containing no carbohydrates and little or no calories. They are called “high-intensity” sweeteners because they are significantly (hundreds, sometime thousands times) sweeter than sucrose (the table sugar). Because artificial sweeteners don’t have carbs, they do not raise your blood sugar levels. As a result, when they are used instead of sugar, artificial sweeteners can help you stay within your desired carbohydrate boundaries when planning your meals. Also, because most artificial sweeteners don’t have any calories, having foods that are made with artificial sweeteners may reduce your calorie intake and contribute to your diet needs. There are six artificial (high-intensity) sweeteners that have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). They include: Acesulfame-potassium (brand names: Sweet One or Sunette) – also known as Ace-K, Aspartame (brand names: NutraSweet, Equal) – also known as “the blue packet”, Saccharin (brand names: Sugar Twin, Sweet Twin, and Sweet’N Low) – also known as “the pink packet”, Sucralose (brand names: Equal Sucralose or Splenda) – also known as “the yellow packet”, Stevia (brand names: Stevia in the Raw, SweetLeaf, Truvia, Sweet Drops, Sun Crystals and PureVia) – also known as “the green packet”, and Neotame. Artificial sweeteners are not hard to come by in everyday life. – You will find them in baked goods, candy, chewing gum, diet drinks, frozen desserts, and light yogurt. Artificial sweeteners are widely available for cooking and baking purposes too. Plus, you can find them in numerous eateries of all kinds as stand-alone sweeteners to add to your tea, coffee, fruit, and cereal. – Everyone knows those blue, yellow, pink, and green packets, stocked up along with sugar packets of different designs. The benefits of artificial sweeteners, those designed in a lab scientific wonders, are quite clear. – The fact that they are often being called “free foods” says it all. Absence of carbohydrates attracts people with diabetes, for whom artificial sweeteners provide an exciting opportunity to enrich their menu with many different desserts, so they can be on par with people without diabetes in this regard. Artificial sweeteners also draw attention of people, who watch their calorie intake, regardless of whether they have diabetes or not. – If you want to lose weight or stay in shape, enjoying some sweet treats in the evening without paying the price on the scale in the morning, sounds like a very attractive proposition. Besides, artificial sweeteners do not increase your chances of developing dental cavities. That is the reason why they are ubiquitously used in many oral hygiene products, among which are toothpastes and mouthwashes. However, some of the artificial sweeteners, even though they are FDA-approved, are better be avoided by some people due to health risks certain sweeteners can cause. Aspartame, for example, despite the fact that more than 200 studies support its safety, is dangerous for people with PKU (phenylketonuria). That’s because it contains an amino acid phenylalanine, which can cause intellectual brain damage, disabilities, seizures and other health problems in people with PKU. Another example is Saccharin. This artificial sweetener has been known around the world for more than 100 years. It can be conveniently used in both cold and hot foods, which makes it a good choice for use in cooking, baking, and preserving. Nevertheless, if you are pregnant or breastfeeding, this common sweetener should be avoided because Saccharin is a weak carcinogen and can cross the placenta to the fetus and stay in your baby's tissue. Other sweeteners are considered safe in this regard as they are not causing any issues during pregnancy or lactation.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||